Principle
This procedure is used to stain mycobacterium tuberculosis and mycobacterium leprae. These bacteria are also called acid fast bacilli. They stain with carbol fuschin, which is a red dye. They retain the dye when treated with acid, which is because of the presence of mycolic acid in their cell wall.
 Reagents
Reagents
- Carbol fuschin (basic dye)
- Mordant (heat)
- 20% sulphuric acid (decolorizer)
- Methylene blue (counter stain) or Malachite green
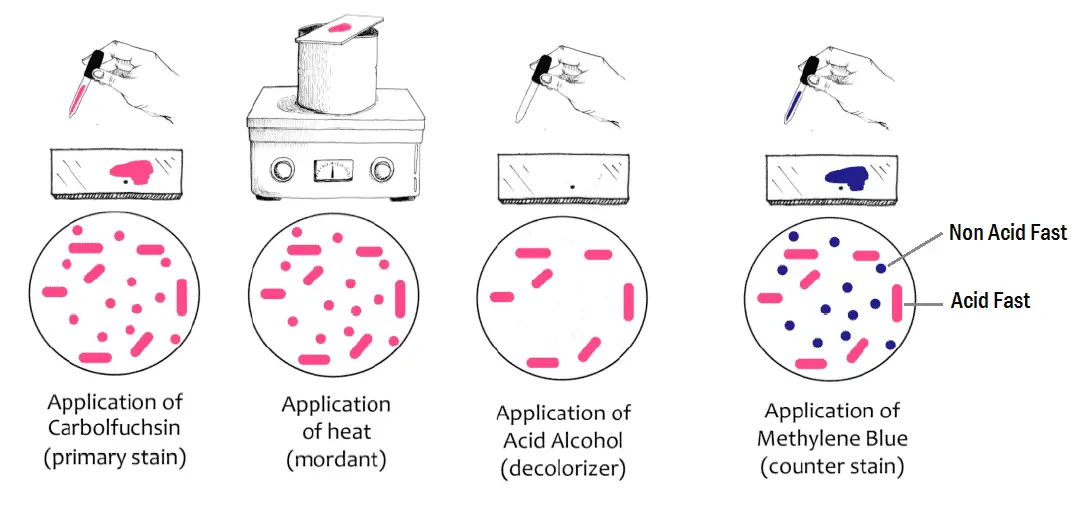
Procedure
- Fix the smear of the specimen over the glass slide, either by heating or alcohol fixation.
- Pour carbol fuschin over smear and heat gently until fumes appear. Do not overheat and allow it to stand for 5 minutes, then wash it off with water.
- Pour 20% sulphuric acid, wait for one minute and keep on repeating this step until the slide appears light pink in color. Wash off with water.
- Pour methylene blue, wait for two minutes, again wash with water
- Allow it to air dry and examine under oil immersion lens.
Result
Acid fast bacilli stain pink, straight or slightly curved rods, at times having beaded appearance. The background appears blue due to methylene blue.
Interpretations
If definite bacilli are seen, report as AFB positive. However, it is better to report the result quantitatively as follows:
- > 10 AFB/high power field –>+++
- 1-10 AFB/high power field –> ++
- 10-100 AFB/100 high power fields –> +
- 1-9 AFB/100 high power fields –> exact number
However if no AFB is seen, write the result as ‘no AFB seen’ and never write negative.
Modifications
a. Mycobacterium leprae
Same method is used with 5% sulphuric acid due to less mycolic acid in cell wall.
b. Nocardia and Legionella
1% sulphuric acid is used
c. Stool Specimen
We use 3% acid alcohol instead of sulphuric acid so as to stain Cryptosporidium parvum.
Hot and Cold Ziehl Neelsen Staining
Hot ZN stain is the usual method in which we heat the smear to enhance the dye penetration.
Whereas in cold ZN staining, instead of heating, we increase the concentration of the basic dye and phenol and incorporate a wetting agent chemical.





No comments:
Post a Comment
Due to the high number of spammy comments we have decided to initiate comment moderation so that we can maintain our quality standards and make good environment for our visitors. Please leave your comment