 The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) virus is spreading rapidly, and scientists are endeavoring to discover drugs for its efficacious treatment in China. Chloroquine phosphate, an old drug for treatment of malaria, is shown to have apparent efficacy and acceptable safety against COVID-19 associated pneumonia in multicenter clinical trials conducted in China. The drug is recommended to be included in the next version of the Guidelines for the Prevention, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Pneumonia Caused by COVID-19 issued by the National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China for treatment of COVID-19 infection in larger populations in the future.
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) virus is spreading rapidly, and scientists are endeavoring to discover drugs for its efficacious treatment in China. Chloroquine phosphate, an old drug for treatment of malaria, is shown to have apparent efficacy and acceptable safety against COVID-19 associated pneumonia in multicenter clinical trials conducted in China. The drug is recommended to be included in the next version of the Guidelines for the Prevention, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Pneumonia Caused by COVID-19 issued by the National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China for treatment of COVID-19 infection in larger populations in the future.
Chloroquine is a medication used to prevent and to treat malaria in areas where malaria is known to be sensitive to its effects. Certain types of malaria, resistant strains, and complicated cases typically require different or additional medication. It is also occasionally used for amebiasis that is occurring outside the intestines, rheumatoid arthritis, and lupus erythematosus. It is taken by mouth.
Chloroquine phosphate
| PubChem CID: | 64927 |
|---|---|
| Structure: | |
| Chemical Safety: |   |
| Molecular Formula: | C18H32ClN3O8P2 |
| Synonyms: | |
| Molecular Weight: |
515.9 g/mol
|
| Parent Compound: | |
| Component Compounds: | |
| Dates: |
|
Chloroquine Phosphate is the phosphate salt of chloroquine, a quinoline compound with antimalarial and anti-inflammatory properties. Chloroquine is the most widely used drug against malaria, except for those cases caused by chloroquine resistant Plasmodium falciparum. Although the mechanism of action is not fully understood, chloroquine is shown to inhibit the parasitic enzyme heme polymerase that converts the toxic heme into non-toxic hemazoin, thereby resulting in the accumulation of toxic heme within the parasite. Chloroquine may also interfere with the biosynthesis of nucleic acids.
| |
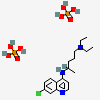

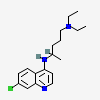 CID 2719 (Chloroquine)
CID 2719 (Chloroquine)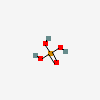 CID 1004 (Phosphoric acid)
CID 1004 (Phosphoric acid)



No comments:
Post a Comment
Due to the high number of spammy comments we have decided to initiate comment moderation so that we can maintain our quality standards and make good environment for our visitors. Please leave your comment